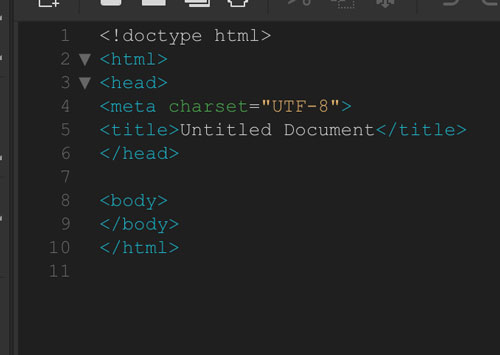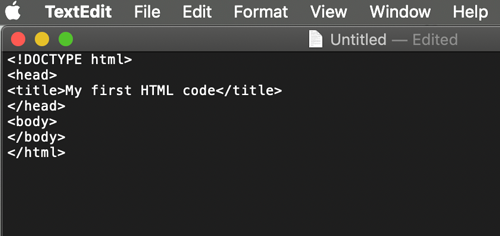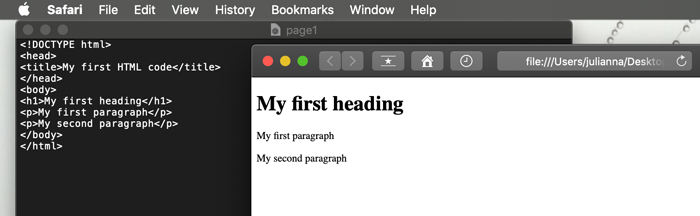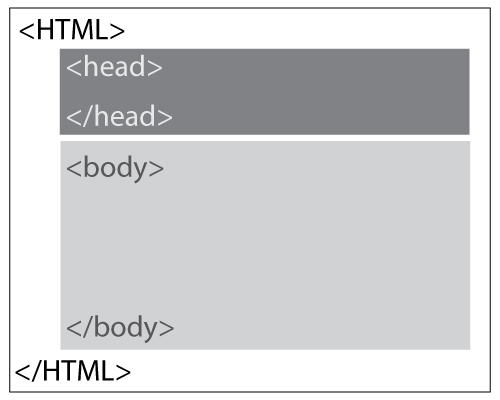
<HTML>
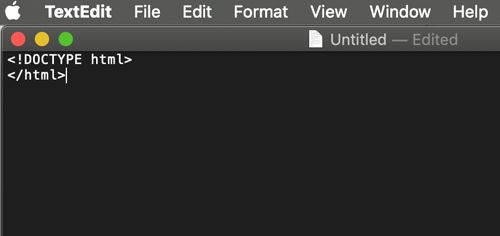
Opening tag. Specifies page as an HTML document
</HTML>
Closing tag. Specifies the end of the document.
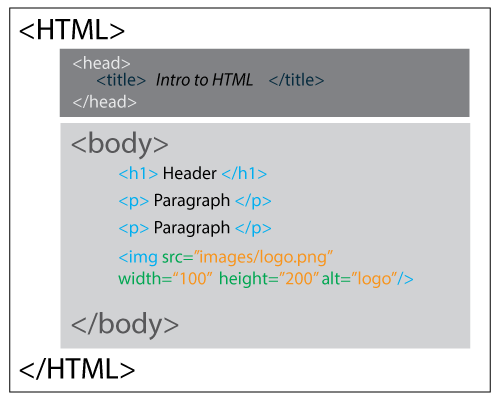
HTML document has two basic parts:
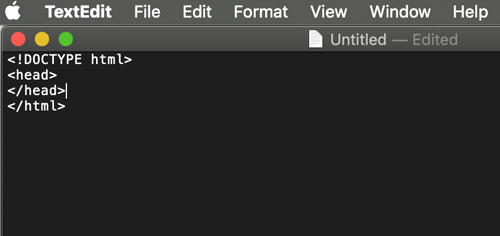
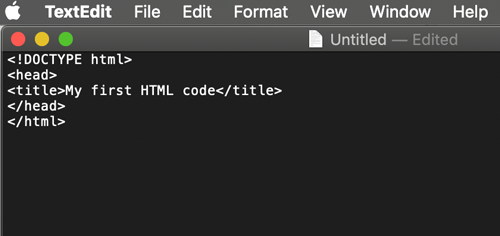
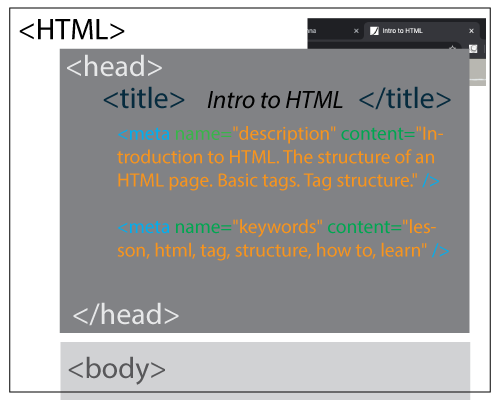
- The <HEAD> section
stores the <title>, keywords, tags, description of a page, styles links, scripts, etc.
</HEAD>
- The <BODY> section
is the viewable section of a page (text, images, media elements, etc)
</BODY>
Each element has an opening tag and a closing tag.
Elements can be nested.

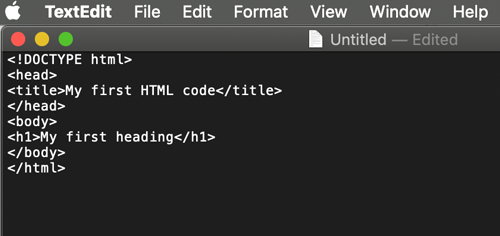
<h3>Text formatting</h3>
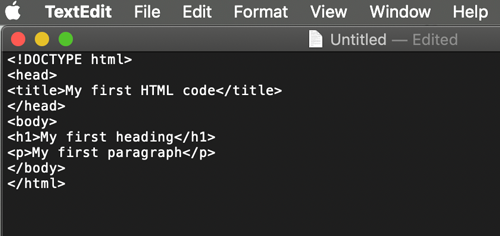
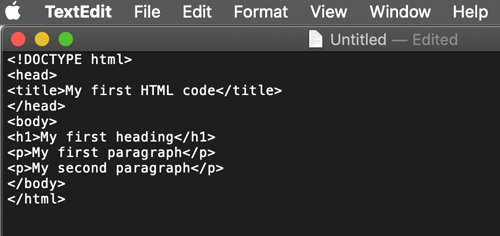
<p>Plain paragraph text</p>
<p><b>This text is bold</b></p>
<p><i>This text is italic</i></p>
<p>This is<sub> subscript</sub> and <sup>superscript</sup></p>
Formatting elements were designed to display special types of text:
inline elements
- <b> - Bold text
- <strong> - Important text
- <i> - Italic text
- <em> - Emphasized text
- <mark> - Marked text
- <small> - Small text
- <del> -
Deleted text
- <ins> - Inserted text
- <code> -
Computer code
- <sub> - Subscript text
- <q> -
A quote
- <sup> - Superscript text
block elements
- <p> -
A paragraph
- <blockquote> -
A quoted paragraph
- <br> - a line break (within a paragraph)
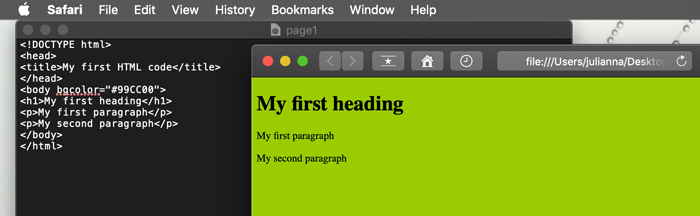
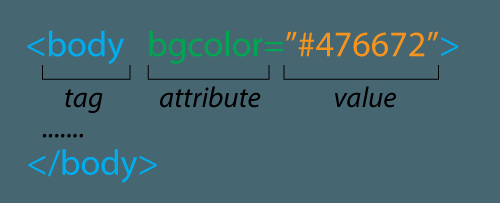
For more text attributes (like font, color, decoration, size - use CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). Use CSS for most of your design needs.
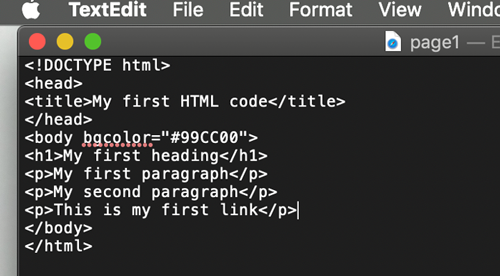
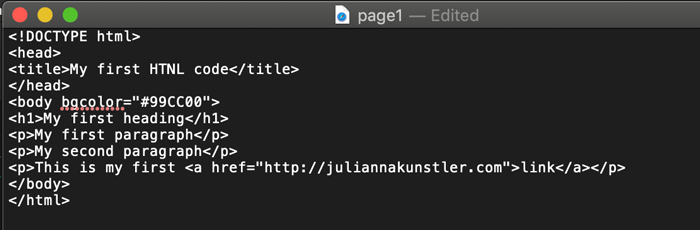
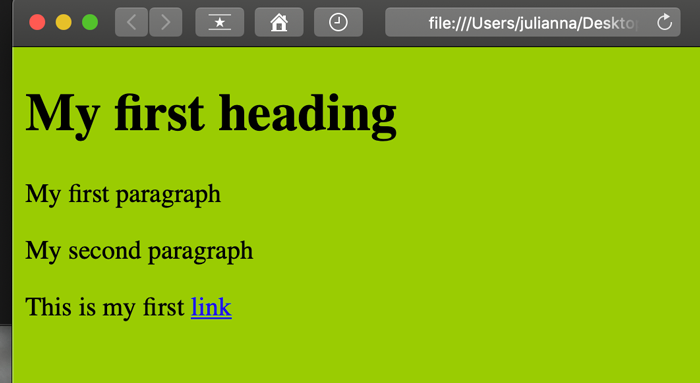
Links
<a> is a link tag.
And, yes, it needs a closing tag too: </a>
This tag needs to have a value - destination.
Here is an example of external link:
<a href="http://w3schools.com/html/html_basic.asp">This is an external link</a>
Internal links (links between pages within you website):
<a href="acgr_web_intro.html">This is a link to another page</a>
... and if you organize your pages in folders:
<a href="folder1/acgr_web_intro.html">This is a link to another page</a>